Mars is a terrestrial planet in the Solar System and the fourth planet from the Sun. Due to its reddish color, coming from the iron oxide prevalent on its surface, it is also called the "Red Planet".
Multiple spacecraft and rovers have been sent to the planet over a long period, starting in the 60s.[BTS 1] In the mid 90s, the first humans landed on the surface of Mars.[1]
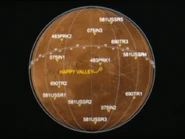
Regions[]
Valles Marineris[]

The Valles MarinerisW is a large system of canyons that runs along the Martian surface. It is located along the equator of Mars and stretches for nearly a quarter of the planet's circumference. Valles Marineris is one of the largest canyons of the Solar System.
Melas Chasma[]
Melas ChasmaW is the widest segment of the Valles Marineris canyon system and is where both American crewed Mars missions set up their bases after landing in 1995.[2] [3]
Gagarin Ridge[]
- Main article: Gagarin Ridge

Gagarin Ridge is a steep ridge at Melas Chasma beside the plain where the first Helios mission set up their Mars base in 1995.
Peckinpah Mesa[]

Peckinpah Mesa is a hill close to the Happy Valley colony. Samantha Massey found some obsidianW there, which Miles Dale sent to his daughter. He wanted to collect more after his wife told him that she was offered $5,000 for it from someone who wanted to make jewelry out of it, but he fell and slid into a trench and had to be rescued by Sam.[4]
Ares Vallis[]

Ares VallisW is an outflow channel on Mars. It appears to have been carved by fluids, perhaps water.
Meridiani Planum[]

The Meridiani PlanumW is a large plain straddling the equator of Mars, covered with a vast number of spherules containing a lot of iron oxide.
Elysium Planitia[]

Elysium PlanitiaW is a broad plain that straddles the equator of Mars. It lies to the south of the volcanic province of ElysiumW, the second largest volcanic region on the planet, after TharsisW.
Planum Australe[]
Planum AustraleW is the southern polar plain on Mars.
Chasma Australe[]

Chasma Australe is a 500 km long and up to 80 km wide canyon up to 1000 m deep at Planum Australe near the Martian south pole.
Gusev crater[]

GusevW is a large Martian crater about 166 kilometers in diameter, formed approximately three to four billion years ago.
Korolev crater[]
- Main article: Korolev crater

The Korolev crater, named after former Soviet chief engineer Sergei Korolev, is an ice-filled impact crater in the northern polar plain Planum BoreumW on Mars.
Exploration[]
Uncrewed missions[]
- See also: Mars rover
Several uncrewed robotic probes and rovers have been sent to the red planet's surface. The first successful landing happened in 1975 when NASA's lander Hermes touched ground undamaged in Ares Vallis and deployed its rover Sojourner, sending home the first ever pictures from the Martian surface.[5] [BTS 2]
Subsequently, more missions with or without rovers were sent to Mars to explore its surface and atmosphere by several countries. In the eraly 90s, India, Turkey and North Korea sent uncrewed probes to the surface of Mars with rendezvous systems sold by Roscosmos.[6]
In mid 1992, the two rovers SpiritW and OpportunityW of NASA's MER missionW were operating inside the Gusev crater and at Meridiani Planum, respectively.[7] [BTS 3]
The robotic probe Endurance was performing long term seismic studies at Elysium Planitia and was still operating in 1995.[8] [9]
In early 1995, NASA's Galileo V probe MPL-2 was doing climate studies at Planum Australe near the Martian south pole.[10] [BTS 4]
Crewed missions[]
In the mid-1990s, the United States, the Soviet Union, and the American private competitor Helios Aerospace raced to land the first humans on the planet.[11] The three competitors all launched their missions during the same launch window in fall 1994, and after an intense race, the first humans believed to set foot on the planet were Grigory Kuznetsov and Danielle Poole.[12]
However, in September 1994, some weeks before the others, the North Korea space program had sent what was believed to be an uncrewed probe to the surface of Mars. Actually, the probe secretly carried two North Korean cosmonauts, Lee Jung-Gil and Park Chol. While the latter was killed during the landing, Lee became the real first man setting foot on Mars on February 8, 1995.[6] [13]
Early 1995, the combined NASA/Roscosmos teams and Helios both set up their own bases on the planet's surface, Happy Valley and Helios base, both inside the canyon Melas Chasma in the Valles Marineris system.[3]
In the late 1990s, the old base transitioned into an international colony of the Mars-7 Alliance nations maintained by Helios, with over 100 habitants.[14] [15]
In 2003, Kelly Baldwin was working at the Carl Sagan Center for Planetary Science on a project to find microbial life in lava tubesW around the Korolev crater and other regions on Mars using kinetically enhanced robots.[16] Some time later, back on Mars, she took a 3-day trip to the crater with her team to set up her experiment.[17] Kelly's robots detected substantial signatures of methane concentration, the heaviest being registered at Korolev crater, but also from Chasma Australe near the Martian south pole.[18]
Gallery[]
Patches[]
Terminology[]
| Term | Plural | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Planum | Plana | Latin word for plateau. It is the IAUW descriptor term for plateaus and high plains. |
| Planitia | Planitiae | Latin word for plain. It is the IAU descriptor term for features which are "low plains". |
| Vallis / Valles | Valles | Latin word for valley. It is used in planetary geology to name landform features on other planets. |
| Chasma | Chasmata | A chasma is a deep, elongated, steep-sided depression. |
| Australis | Latin word for southern or the south. | |
| Borealis | Latin word for northern or the north. |
Behind the scenes[]
- ↑ In reality, the first successful flyby on Mars was by NASA's Mariner 4W spacecraft in 1965.
- ↑ First Mars rover
In reality, the first NASA rover arrived on Mars in 1997 only, with the PathfinderW mission. The rover was called Sojourner, like in the show as well, and was also landed with the help of airbags, but in reality there was no lander called Hermes.
In the novel and film The Martian, Hermes was the spacecraft to transport astronauts from Earth to from Mars' orbit and back. - ↑ MER mission
NASA's MER missionW was a real mission, sending two robotic rovers to the Martian surface in summer 2003, both landing on the planet in January 2004. The rover SpiritW landed within the impact crater GusevW and was operational until March 2010. Its sister rover OpportunityW landed in Meridiani PlanumW and was operational until June 2018.
In the For All Mankind timeline, both rovers appear to have the same missions at the same locations, but are in operation over 10 years earlier than in reality. - ↑ Galileo
In reality, the Galileo projectW was a robotic space program of NASA that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as several other Solar System bodies. It launched in fall 1989 aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis and arrived at Jupiter in December 1995. However, there was no "Galileo V" in reality, the spacecraft's name was just GalileoW.
In For All Mankind, Galileo V appears to be the show's version of the real-life Mars Polar LanderW, given its name (MPL-2), its mission (climate study), and its location (Planum AustraleW). The Mars Polar Lander, also Mars Surveyor '98, was a NASA/JPL robotic lander launched in January 1999 to study the climate of Planum Australe near the Martian south pole. However, the lander was lost after its descent phase and never established communication.
In For All Mankind, the probe appears to have landed several years earlier and is in operation in March 1995.
See also: mars.nasa.gov: Mars Polar Lander
mars.nasa.gov: Mars Polar Lander
- ↑ The Mars patch bears resemblance to the patch belonging to the AresW rockets from NASA's now defunct Constellation programW.
See also[]
External links[]
 Mars on Wikipedia
Mars on Wikipedia Valles Marineris on Wikipedia
Valles Marineris on Wikipedia Melas Chasma on Wikipedia
Melas Chasma on Wikipedia trek.nasa.gov: Mars Trek - NASA
trek.nasa.gov: Mars Trek - NASA
References[]
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 3
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 3, Episode 4: "Happy Valley"
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 For All Mankind TV Series - Season 3, Episode 6: "New Eden"
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 4, Episode 1: "Glasnost"
- ↑ Bonus Video: One Giant Leap: 1975-1982 - Mars Landing (1975)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 For All Mankind TV Series - Season 3, Episode 9: "Coming Home"
- ↑ Season 3, Episode 2: "Game Changer" (Mission status board @ 57:45) → Screenshot
- ↑ Season 3, Episode 2: "Game Changer" (Mission status board @ 07:47) → Screenshot
- ↑ Season 3, Episode 6: "New Eden" (Mission status board @ 44:50) → Screenshot
- ↑ Season 3, Episode 7: "Bring It Down" (Mission status board @ 43:00) → Screenshot
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 3
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 3, Episode 5: "Seven Minutes of Terror"
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 3, Episode 10: "Stranger in a Strange Land"
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 4, Episode 1: "Glasnost"
- ↑ Bonus Video: Leap Into a New Millenium: 1996-2001 - The Mars-7 Alliance (1997)
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 4, Episode 2: "Have A Nice Sol"
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 4, Episode 8: "Legacy"
- ↑ For All Mankind TV Series - Season 4, Episode 9: "Brazil"












![Mars Patch.png (363 KB) Nasa Mars patch[BTS 5]](https://static.wikia.nocookie.net/for-all-mankind/images/0/0d/Mars_Patch.png/revision/latest/scale-to-width-down/120?cb=20221012181903)











